De-heroification … dispelling some Reagan myths
Now that the hoopla of February's first weekend has faded, let’s hope the deification process fades as well. It must have been such a downer for the Reaganites and their 100th birthday celebrations to have to compete with the NFL and the most watched Super Bowl ever…the gall to schedule such an event on the holiest of days! Amidst all the reminiscing and nostalgia, I did happen to see a few articles not as admiring, such as Michael Kinsley's on Slate. I like this part:
In the economic sphere (discussed in last week's column), the Reagan hagiographers give him credit for things he intended that never happened, such as smaller government. On the world stage, they credit him for things he never intended that did happen.
 I'm not going to get into the myriad of philosophical elements of Reagan's legacy on what he did and didn't do and what gets attributed correctly or not. I don't have the time, or the inclination, and there are a host of Gipper love books and a couple like Will Bunch's Tear Down This Myth: How the Reagan Legacy Has Distorted Our Politics and Haunts Our Future for your reading pleasure.
It's human nature to see things from one's too often myopic viewpoint and human nature to remember things they way we want, to the point of manufacturing memories that just aren't true. Such is the case with Reagan and that nostalgia. Longing for the days that never were. And the political right and its Murdoch media arm are very good at enhancing the myth that is the goal of the Reagan Legacy Project, "recalling" those good old days of Reagan.
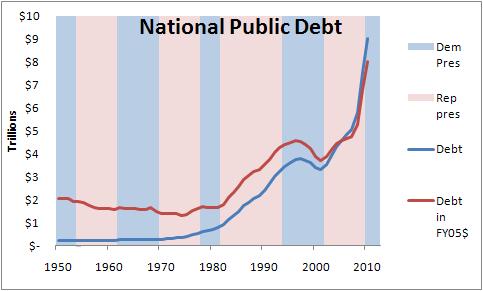
Truth or not, there are several topics that are now commonly tied to Reagan's legacy; myths of smaller government, lower taxes, less spending. And most people have no idea how much the debt and deficit grew under Reagan.
The military has a nice term known as BLUF - which stands for Bottom Line Up Front. This is going to get tedious, so I'll cut to the chase:
I'm not going to get into the myriad of philosophical elements of Reagan's legacy on what he did and didn't do and what gets attributed correctly or not. I don't have the time, or the inclination, and there are a host of Gipper love books and a couple like Will Bunch's Tear Down This Myth: How the Reagan Legacy Has Distorted Our Politics and Haunts Our Future for your reading pleasure.
It's human nature to see things from one's too often myopic viewpoint and human nature to remember things they way we want, to the point of manufacturing memories that just aren't true. Such is the case with Reagan and that nostalgia. Longing for the days that never were. And the political right and its Murdoch media arm are very good at enhancing the myth that is the goal of the Reagan Legacy Project, "recalling" those good old days of Reagan.
Truth or not, there are several topics that are now commonly tied to Reagan's legacy; myths of smaller government, lower taxes, less spending. And most people have no idea how much the debt and deficit grew under Reagan.
The military has a nice term known as BLUF - which stands for Bottom Line Up Front. This is going to get tedious, so I'll cut to the chase:
In raw numbers not adjusted for inflation, Reagan increased federal spending by $466B (69%) over what he inherited, averaged a %177B deficit (+180%), added $1.40 trillion to the debt (+178%), enjoyed a pretty substantial increase in the GDP (+77%), but increased the debt to GDP ratio by 15%. Even adjusted to a FY2005 baseline to account for inflation, Reagan still increased federal spending by 22%, averaged a deficit that was 99% more than Carter's average, increased the public debt by 100%, and as the adjusted GDP increase was only 28%, that 15% increase in debt to GDP was a lot more substantial. Reagan added 13,000 non-defense federal employees - the IRS grew despite his wishes. (Clinton decreased the non-defense federal workforce by 99,000.)I'll deal with each piece individually, but that's it in a nutshell. If you want to know more and how I determined this, read on...