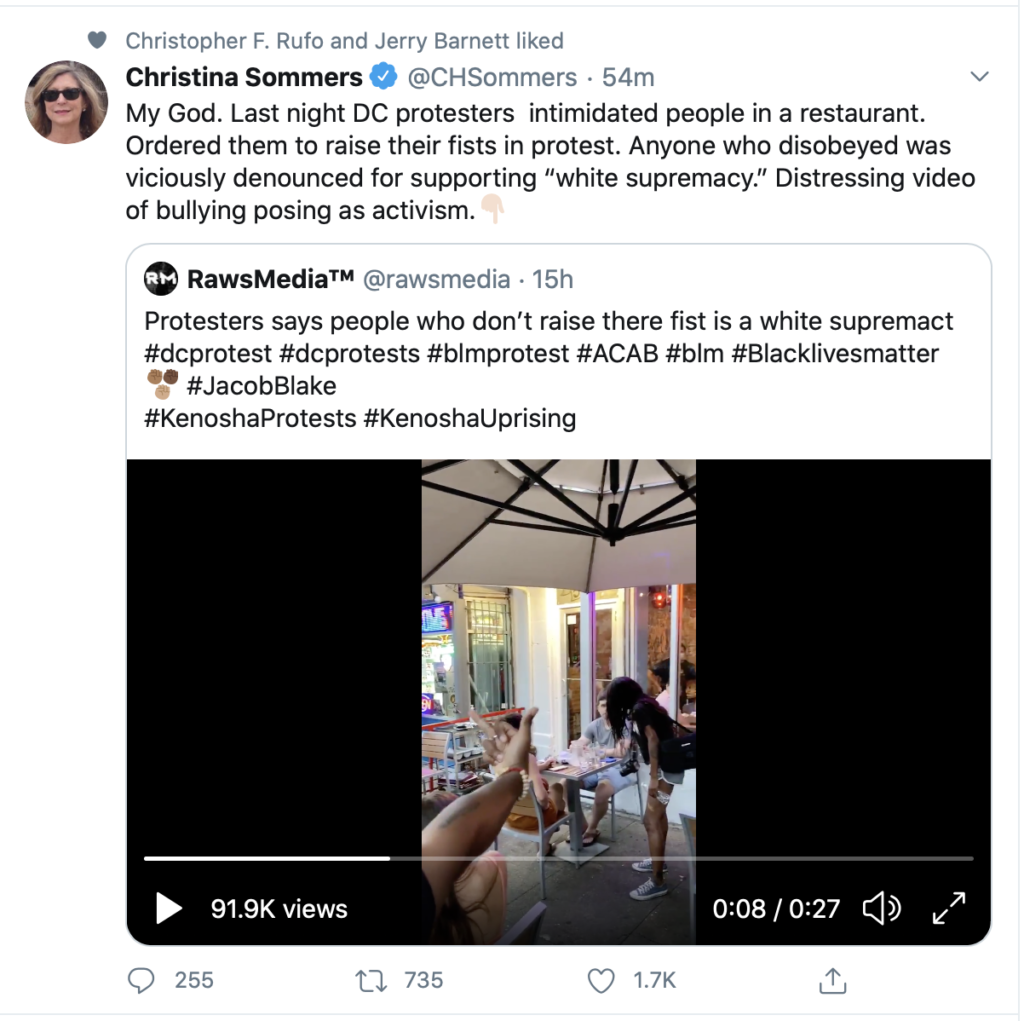
Babygate: Where People Allow Skin Color to Interfere with Basic Human Kindness
Have you heard about "Babygate"? The crux of the problem is that a white man affectionately held a Black friend's Black baby on his lap, at the friends's request during a meeting of the NYC Community Education Council. Members of the Council complained, indicating that this was "harmful" and that it "hurts people." The formal written accusation contained the following:
The letter characterized the lap incident as harmful: “Imagine the insult and emotional injury any thinking person, especially a person of color, suffered when they witnessed this scene and heard that comment,” it stated, calling them “shocking, disgusting, offensive, and racially incendiary.” It demanded that Wrocklage resign, claiming that allowing such incidents to continue without consequences “will only further empower the perpetuation of similar racist behaviors.
When the man who held the baby was called out, he challenged the accusers to state why this was racist. The accusers could not explain why this was racist. They told him that he needed to read Robin DiAngelo. This incident illustrates how crazed we are getting. "Anti-racist" ideology is has successfully turned innocent human kindness into a bad thing.
This recent incident and its aftermath were described in detail, then analyzed by Conor Friedersdorf of The Atlantic in an article titled "Anti-racist Arguments Are Tearing People Apart: What a viral story reveals about contemporary leftist discourse." An excerpt:
Folks who have different ideas about how to combat racism should engage one another. They might even attempt a reciprocal book exchange, in which everyone works to understand how others see the world. A more inclusive anti-racist canon would include Bayard Rustin, Albert Murray, Henry Louis Gates, Zadie Smith, Thomas Sowell, Shelby Steele, Danielle Allen, Randall Kennedy, Stephen Carter, John McWhorter, Glenn Loury, Barbara and Karen Fields, Thomas Chatterton Williams, Adolph Reed, Kmele Foster, Coleman Hughes, and others.
As long as sharp disagreements persist about what causes racial inequality and how best to remedy it, deliberations rooted in the specific costs and benefits of discrete policies will provide a better foundation for actual progress than meta-arguments about what “anti-racism” demands.
Meanwhile, in Portland, Oregon, Violence Continues
Violence on the street every night in Portland, Oregon, despite the departure of federal law enforcement two weeks ago. The senseless destruction and violence is described in detail by the Washington Post. Here's an excerpt:
The weeks of destruction and intense clashes with police following the death of George Floyd in Minneapolis in late May have spurred angry backlash from Portland officials and some residents. Tensions have risen in recent weeks following a period of relative calm after federal law enforcement left Portland last month. . . . Tuesday night’s fire damaged important county resources that have nothing to do with policing, officials said, including the county’s Office of Community Involvement, which aims to engage historically marginalized communities in local political decisions about social services and the distribution of public resources.“The lobby where the first same-sex marriage in Oregon took place, and where millions of pieces of personal protective equipment are being distributed to help our community battle covid-19, was damaged,” Multnomah County Chair Deborah Kafoury said in a statement.
Total silence from the New York Times for two weeks. Nothing from NPR for the past 10 days. It's like Portland doesn't exist . . . or perhaps these stories don't fit the official narrative.
Concern with Obesity, Fat-Shaming and Racism
People who don't know me well sometimes assume that it's easy for me to keep my weight down. This is completely untrue. I constantly watch what I eat. I constantly force myself to exercise and I make myself get on the scale several times each week. If I don't do these things I will gain 2 or 3 pounds per month. I've repeatedly and unwittingly run the experiment of not paying attention to my weight during my life. Each time I fall off the rails, I have had to call a stop to the nonsense and declare war on my fat. Over the past 30 years, this has led me to begin ever new rounds of weight loss boot camp (on my own, at home) where I've worked hard to lose 35, 20, and 20 pounds, as well as various smaller amounts of weight. I'm currently in yet another (minor) boot camp that will end when I lose 5 more pounds. This is my plight, my burden and my opportunity if I am going to maintain a body that feels good and fits my clothes. I also want to avoid risks of diabetes, cancer, heart disease, strokes and other illnesses associated with excess weight.
Whenever I find out that friends are trying to reduce their size, I encourage them and celebrate their successes with them. I silently applaud when I see obese people I don't know exercising at the park Good for them! I hope they reach their goals!
Increasingly, however, the excesses of the "body positivity" movement invade my thought process, occasionally making me do mental double-takes. Body positivity is a double-edged sword:
On the one hand, body positivity—the attitude associated with the movement—aims to try to help overweight and obese people (especially women—see also, fat feminism—and sometimes, when intersectionally analyzed, specifically black women) accept themselves and their overweight status as they are so that negative emotions are not tied up with it. This, of course, has the direct benefit of helping people not feel bad about themselves for a state of facts about the world (weight, BMI, body fat percentage, etc.), which can be demotivating and hinder weight loss attempts (or, which can just be mean and bullying—see also, fat shaming).
On the other hand, body positivity tends to rather aggressively deny any connection between weight status, including obesity, and health (see also, healthism). It rejects such connections as a “medicalized narrative” (see also, regulatory fiction). This rejects mountains of medical evidence suggesting otherwise, that being overweight and especially obese correlates strongly with and causes a number of serious health issues. This view relies upon seeing body weight status and obesity ultimately as a social construction that is used to create an unjust power dynamic that discriminates against and oppresses fat people. Activism in the body-positive movement often encourages overweight people not to want to lose weight (sometimes as a means of identity politics—see also, identity-first), which is irresponsible, at best (e.g., a book in the movement is titled You Have the Right to Remain Fat).
I agree with the benefits of body positivity described above. Overweight people should not be shamed. They should not be shunned. Doing these things is cruel and destructive. We should recognize every other person to be a precious human being. It all starts with I and Thou, Martin Buber's version of the golden rule.
That said, how can it possibly be bigoted when I work hard to be healthy and look better by losing weight. How can I possibly be acting out of bigotry to the extent that I encourage others to reach their weight loss goals? It's not. For background, see this article on Woke attitudes toward obesity at New Discourses. This is shut-up ("Woke") culture doing what it does best: halting important and necessary conversations under the guise of combating alleged discrimination. Today's excess is an article by CBS featuring a sociology professor who claims that concern with obesity is veiled racism.
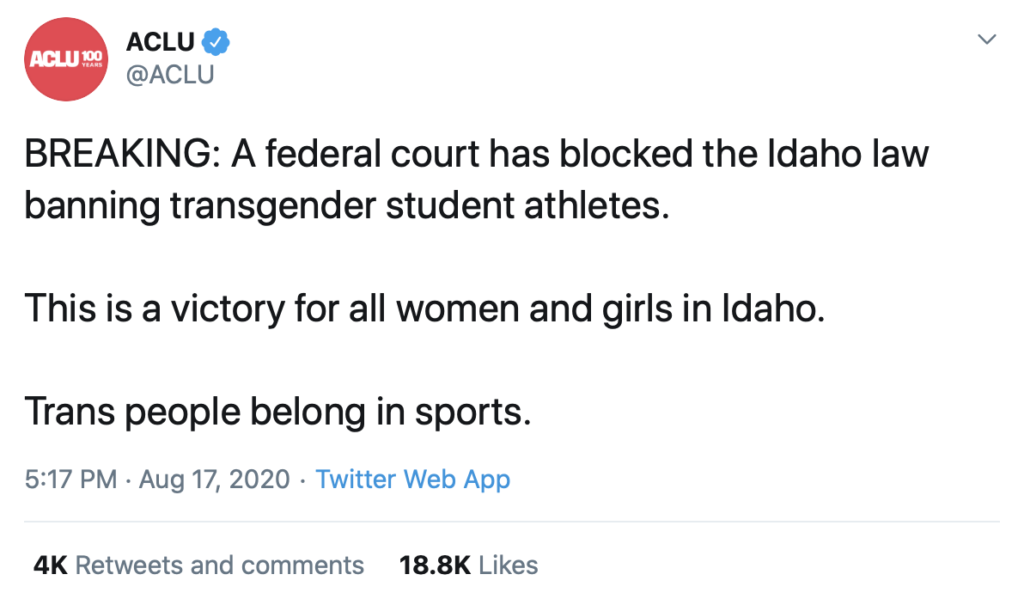
Judge Gives Green Light for Transwomen Athletes to Compete in Women’s Sports
The ACLU is doing a victory lap on a case that risks demoralizing many woman athletes and dissuades them from competing at all. Here's the ACLU Tweet:
We now have a competing-frames argument like we do in the abortion debate (my body vs. don't kill babies). In transgender sports, the competing frames are A) It is insulting and unfair to exclude trans people from women's sports, versus B) Trans women are so much stronger, faster and larger than bio women (because they went through puberty as men) that they are dominating the competition. This competing Frame flips between two principles and also flips between the perspectives of the two parties to this dispute.
In reaction to the ACLU Tweet many people are applauding this court decision as kind and decent, the correct thing to do for trans women. Laudable first principles are important, but so are the overall consequences for women's sports. What if this court case destroys the careers of aspiring women athletes in order to invite athletes who went through puberty as men to compete as women? I believe that this decision will demoralize many women athletes and convince them give up careers as women athletes. Regardless of how well-intentioned it is to be "inclusive," this decision is likely to hurt attendance and destroy the carefully constructed spaces that most women athletes want and need in order to fairly compete. My concerns are echoed by the concerns of many women who have responded to the ACLU Tweet. Here are some excerpts from numerous comment Tweets to the above Tweet, all of them by women:
This is definitely not a victory for girls and women. It is a victory for trans identified males.
How is this a victory? This is a kick in the teeth for women in sports
Girls are going to drop out of sports if they know that they don't have a fair competition.
All these transwomen are way taller than the average woman/girl yet even seeing this obvious physical difference they deny the Male body that these transwomen inhabit. Why don't female hormones shorten these transwomen to a normal woman's height? A: Because Trans science is false
If women and girls to walk off the field, who will biological men race /play against then ?
Seriously, this left has lost its mind. I’m tired of wondering where sanity went and expecting it to come back.
The fact that every left wing person in this country isn’t screaming about the damage this will do to our girls tells me the left I knew no longer exists.
Let this sink in. A rights organisation is fighting not to keep boys out of girls sports but to PUT THEM IN.
This is so worrisome. A female cannot compete with a transwoman, especially if they transitioned after male puberty. Most bone and muscle mass for a transwoman will have already been built as a male. For a biological woman to compete, she would have to take testosterone.
A tragedy for women/girls! The ACLU actively works against women/girls to steal their existing rights! The ACLU attempts to steal opportunities of girls to compete, steal their scholarships.
What’s the point? Sport is competitive. Looking at World Rugby’s analysis, allowing TW to play against women is not remotely competitive. It is dangerous. Who wants to compete in, or watch that?
It will kill women’s sport taking the little revenue it had with it.
- Go to the previous page
- 1
- …
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- …
- 124
- Go to the next page