COVID Face Masks and Middle East Politics
Below is a recent photo from Washington University posted on Facebook.
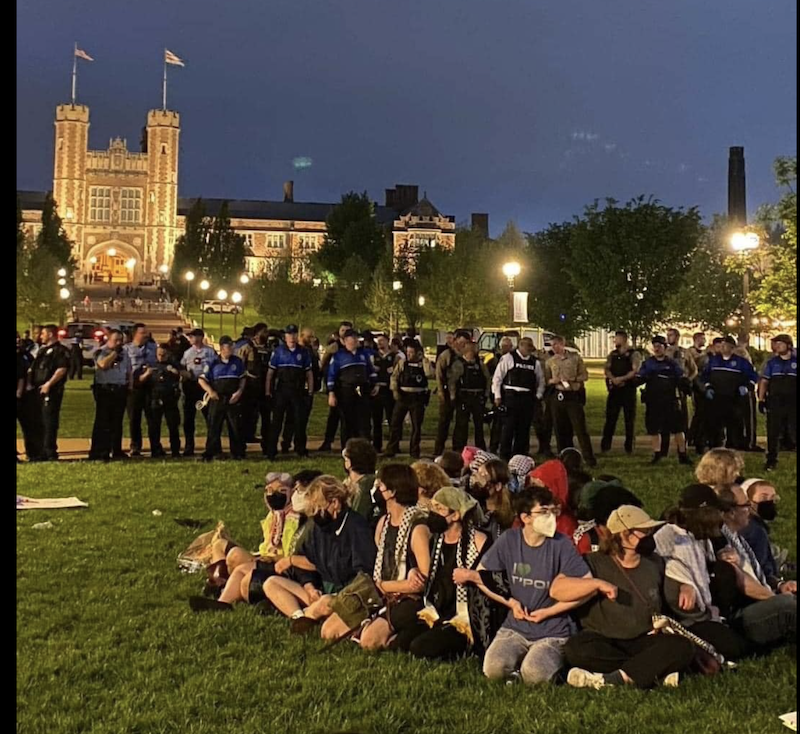

Notice all the participants wearing COVID face masks. The COVID pandemic is long over and more than a year ago, the Cochran study found no evidence that face masks are effective to prevent spread of COVID.
What do these face masks have to do with Middle East politics? Nothing. What do totally unnecessary post-pandemic face masks have to do with tribalism? Everything. The masks serve as badges of in-group membership. They function the same way that fancy suits do for trial lawyers and executives. The same way that buying pre-torn jeans serve for young women or that wearing ashes on foreheads serve as badges of group belonging to Catholics. For more than 100 posts on Ingroup-Outgroup dynamics at this website, click here.
Intelligent People Excel at Fooling Themselves
This is an excellent 15-min video by After Sokol. Psychologist have found that highly intelligent people are great at fooling themselves, especially when they form tribes.
Here is an excerpt from the video:
Kahan and a team of researchers found that test subjects who scored highest in numeracy were better able to objectively evaluate statistical data when told it related to a skin rash treatment, but when the same data was presented as relating to a polarizing subject, gun control, those who scored highest on numeracy actually exhibited the greatest bias. The correlation between intelligence and ideological bias is robust, having been found in many other studies … These studies found stronger biases in clever people on both sides of the aisle.And since such biases are mutually contradictory, they can't be a result of greater understanding. So what is it about intelligent people that makes them so prone to bias? To understand we must consider what intelligence actually is. In AI research, there's a concept called the orthogonality thesis. This is the idea that an intelligent agent can't just be intelligent, it must be intelligent at something because intelligence is nothing more than the effectiveness with which an agent pursues a goal. Rationality is intelligence in pursuit of objective truth. But intelligence can be used to pursue any number of other goals. And since the means by which the goal is selected is distinct from the means by which the goal is pursued. The intelligence with which an agent pursues its goal is no guarantee that the goal itself is intelligent.
As a case in point, human intelligence evolved less as a tool for pursuing objective truth than as a tool for pursuing personal well being, tribal belonging, social status, and sex. And this often required the adoption of what I call fashionably irrational beliefs and fibs which the brain has come to accept that. Since we're a social species, it is intelligent for us to convince ourselves of irrational beliefs if holding those beliefs increases our status and well being. Dan Kahan calls this behavior, identity protective cognition, or IPC, by engaging in IPC people bind their intelligence to the service of evolutionary impulses, leveraging their logic and learning not to correct delusions, but to justify them. Or, as the novelist Saul Bellow put it a great deal of intelligence can be invested in ignorance when the need for illusion is deep. What this means is that while unintelligent people are more easily misled by other people, intelligent people are more easily misled by themselves.
See also, the work of Dan Sperber, discussed here.
About Political Factions
It distresses me that so many educated people embrace tribal politics, regardless of what tribe affiliate with. The Founders of the U.S. rightfully feared that factions would be our undoing as a country. For many people, it's as though the Enlightenment never occurred. Sarah Pruitt offers the historical background:
Today, it may seem impossible to imagine the U.S. government without its two leading political parties, Democrats and Republicans. But in 1787, when delegates to the Constitutional Convention gathered in Philadelphia to hash out the foundations of their new government, they entirely omitted political parties from the new nation’s founding document.
This was no accident. The framers of the new Constitution desperately wanted to avoid the divisions that had ripped England apart in the bloody civil wars of the 17th century. Many of them saw parties—or “factions,” as they called them—as corrupt relics of the monarchical British system that they wanted to discard in favor of a truly democratic government.