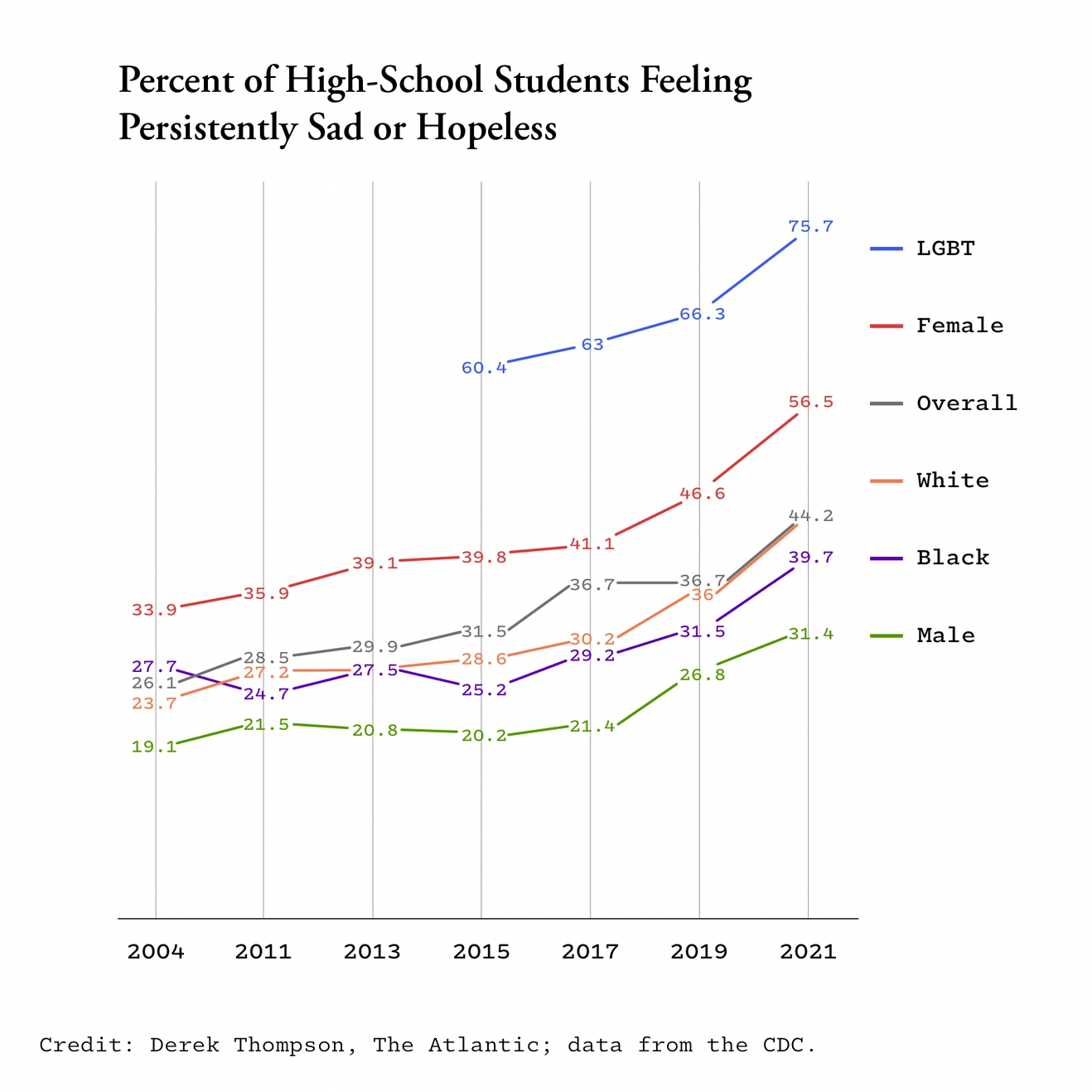
American Teenagers in Crisis
The above is from Derek Thompson's article in The Atlantic: "Why American Teens Are So Sad: Four forces are propelling the rising rates of depression among young people."
The four forces are:
1. Social-media use
Social media isn’t like rat poison, which is toxic to almost everyone. It’s more like alcohol: a mildly addictive substance that can enhance social situations but can also lead to dependency and depression among a minority of users.
2. Sociality is down.
More social media means less unstructured face-to-face time with others.
3. The world is stressful—and there is more news about the world’s stressors
"Fears about finances, climate change, and viral pandemics are smashing into local concerns about social approval and setting oneself up for success."
4. Modern parenting strategies
Today's helicopter parents are depriving their teenagers of opportunities for learning how to tolerate discomfort and developing a sense of personal competence. Further, Thompson notes "a broad increase in an “accommodative” parenting style."
In conclusion, here is an excerpt from Thompson's article:
The world is overwhelming, and an inescapably negative news cycle creates an atmosphere of existential gloom, not just for teens but also for their moms and dads. The more overwhelming the world feels to parents, the more they may try to bubble-wrap their kids with accommodations. Over time, this protective parenting style deprives children of the emotional resilience they need to handle the world’s stresses. Childhood becomes more insular: Time spent with friends, driving, dating, and working summer jobs all decline. College pressures skyrocket. Outwardly, teens are growing up slower; but online, they’re growing up faster. The Internet exposes teenagers not only to supportive friendships but also to bullying, threats, despairing conversations about mental health, and a slurry of unsolvable global problems—a carnival of negativity. Social media places in every teen’s pocket a quantified battle royal for scarce popularity that can displace hours of sleep and makes many teens, especially girls, feel worse about their body and life. Amplify these existing trends with a global pandemic and an unprecedented period of social isolation, and suddenly, the remarkable rise of teenage sadness doesn’t feel all that mysterious, does it?