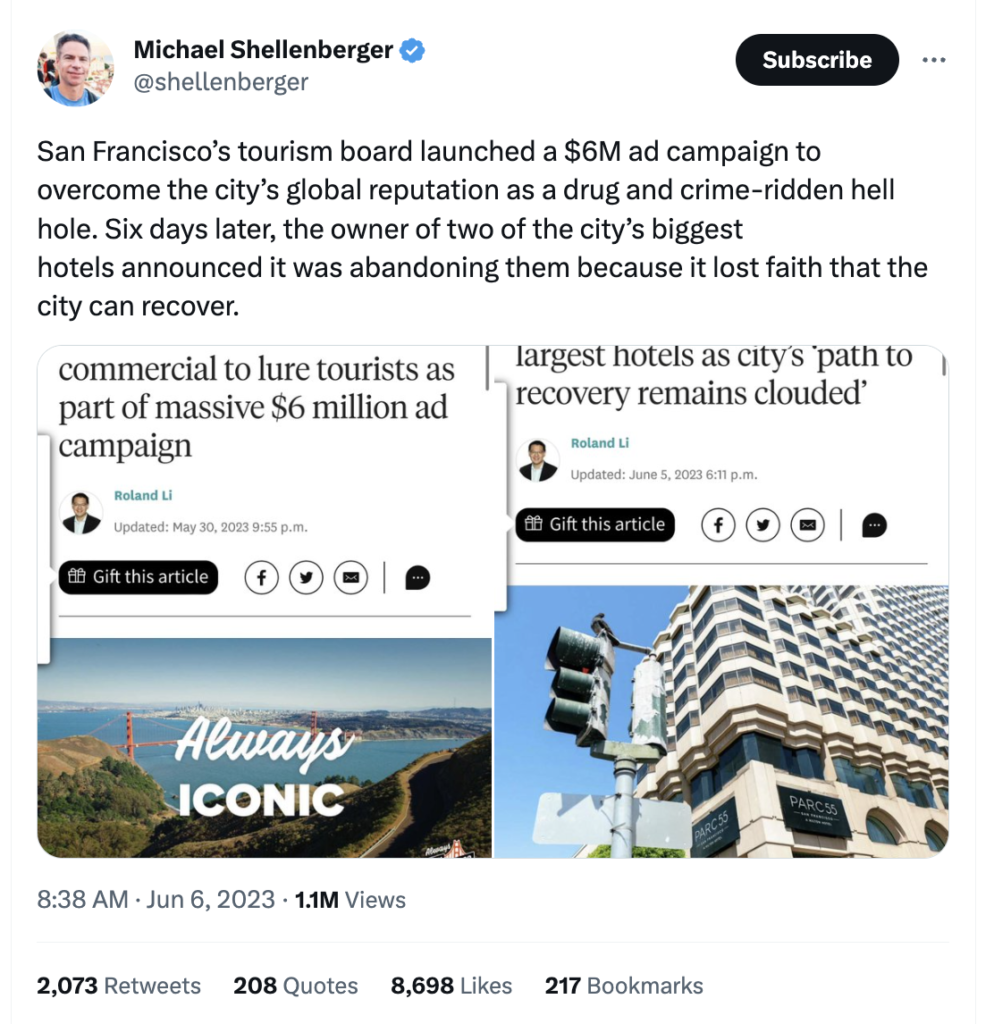
Meaningful Conversation is Like Sex
Last week Bret Stephens gave a talk on the culture of free speech at the University of Chicago. I often don't agree with Stephens, but I think he's on target with this commentary Here is an excerpt:
I hope you do, whether you choose to lead a private or a public life. And I hope you do so by writing your own version of “The Joy of Argument” — which is like a similarly titled book from 50 years ago, updated for an era that has become curiously and depressingly afraid of both. The joy of argument is not about “owning” or “destroying” or otherwise trying to disparage, caricature or humiliate your opponent. On the contrary, it should be about opposition and mutuality, friction and delight, the loosening of inhibitions and the heightening of concentration, playfulness and seriousness, and, sometimes even, a truly generative act.
Yes, I am comparing great arguments to great sex. But the analogy bears a brief follow-through because, in the last analysis, the only way in which we are going to create institutions in which independent thought and free expression flourish isn’t through a declaration of principles, however well constructed it may be — at best, those principles can only lay the ground for what we are trying to achieve. Nor can it be on account of some worthy but abstract goal, like the health of democracy — which, again, is wonderful, but rarely motivates people to action.
We are going to succeed at the task only when we persuade others, and ourselves, that these things you’ve all been doing at the University of Chicago for the past few years — discussing and debating and interrogating and doubting and laughing and thinking harder and better than you ever did before — aren’t the antithesis of fun. They are the essence of it. They make up the uniquely joyful experience of being authentically and expressively and unashamedly yourself and, at the same time, having a form of honest and intimate contact with others who, in their own ways, are being authentically and expressively and unashamedly themselves.
He is well aware that many of us don't speak up. Why? He lists four reasons:
1. "First, the problem isn’t that people aren’t smart. It’s that they are scared."
2. Some arguments that sound persuasive are severely defective. "Will you be able to notice the underlying flaw in an idea when the arguments for it sound so persuasive?
3. It's pleasurable to bask in the emotional warmth of one's tribe: "They go along to get along, because the usual emotional companion to intellectual independence isn’t pride or self-confidence. It’s loneliness and sometimes crippling self-doubt. Is that a price you are willing to pay?"
4. Our culture fails to protect those willing to earnestly participate in wide-open conversations: "Does the culture of a society, or of an institution, encourage us to stand out or to fit in; to speak up or to bury our doubts? Does it serve as a conduit to groupthink, or as an obstacle to it?"