I was reading The Cosmic Story of Carbon-14 and had a thought involving the Abundance of the Elements and isotopes. We now know how the elements formed, and have measured their relative abundances for a while and across the universe. The theory of how they form matches every measurement. Basically, Hydrogen and traces of Helium have been around for over a dozen billion years. Heavier elements form when the mass attraction of enough hydrogen squishes a star's core to fuse together helium and some lithium, a star is born.
All the rest form from the extreme compression and sudden release of supernovas. All that hydrogen and helium (basically protons and neutrons as there are no attached electrons at those pressures) are squeezed to dissolve into a quark soup then expanded and quick-frozen before they can push themselves apart. What is expected from this is an asymptotic curve of element abundances with hydrogen at the high end, and slight peaks forming at iron, xenon, and lead (particularly stable elements).
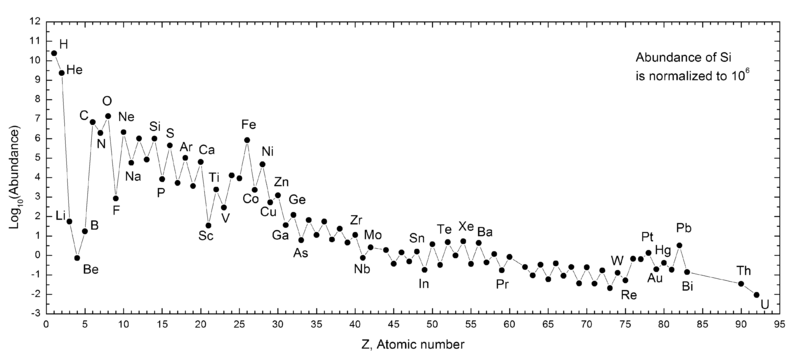
This is what is measured in our solar system:
 Don't let the zig-zag pattern confuse you. Odd numbered elements are harder to hold together than even ones; each pair of protons needs a pair of neutrons to let them stick together. But odd numbered ones have that odd pair of singles; they are just less likely to form.
But how does Carbon-14 fit in? What really freezes out from the splash of quark soup is not so much elements as isotopes. Every possible isotope forms in its proportional place along the curve. Then the unstable ones follow a decay chain until either they reach a stable element, or we measure them somewhere along the way. Uranium, for example, has 3 isotopes that last long enough to have hung around the 5 billion years or so for us to measure them. Technetium, on the other hand, is only found today as a decay byproduct from other elements.
So back to carbon. The three most common isotopes of carbon weigh 12, 13, and 14 atomic units (aka fermion masses: neutrons or protons). C-12 is most of it, C-13 is 1.1%, and C-14 is about 1/1,000,000,000,000 part of it. Carbon 13 is an odd-numbered isotope, and therefore intrinsically rare. Carbon-14 has a half life of 5,730 years. So if it were created in the expected normal proportion to carbon-12 billions of years ago, we would expect to not see any left. Where it all comes from is recent nuclear collisions between protons (cosmic rays) and nitrogen in the upper atmosphere. (More details here).
We see the amount of carbon-14 that we'd expect for a regular continuous influx of cosmic rays that we do measure. But if all the elements had been made 10,000 years ago, we'd expect about C-14 to be about 1/4 of the total carbon, not the mere 1/1012 of it that we know is produced by cosmic ray collisions.
It turns out that comparing the abundance of isotopes of any element indicates the age of the planet to be between 4,000,000,000 and 5,000,000,000 years.
But what (I can predict this argument) if God created the elements with the isotope distributions intentionally skewed to just look like everything is that old? The old God-is-a-liar and created the young world old to eventually test faith of careful observers argument. I counter this with:
Don't let the zig-zag pattern confuse you. Odd numbered elements are harder to hold together than even ones; each pair of protons needs a pair of neutrons to let them stick together. But odd numbered ones have that odd pair of singles; they are just less likely to form.
But how does Carbon-14 fit in? What really freezes out from the splash of quark soup is not so much elements as isotopes. Every possible isotope forms in its proportional place along the curve. Then the unstable ones follow a decay chain until either they reach a stable element, or we measure them somewhere along the way. Uranium, for example, has 3 isotopes that last long enough to have hung around the 5 billion years or so for us to measure them. Technetium, on the other hand, is only found today as a decay byproduct from other elements.
So back to carbon. The three most common isotopes of carbon weigh 12, 13, and 14 atomic units (aka fermion masses: neutrons or protons). C-12 is most of it, C-13 is 1.1%, and C-14 is about 1/1,000,000,000,000 part of it. Carbon 13 is an odd-numbered isotope, and therefore intrinsically rare. Carbon-14 has a half life of 5,730 years. So if it were created in the expected normal proportion to carbon-12 billions of years ago, we would expect to not see any left. Where it all comes from is recent nuclear collisions between protons (cosmic rays) and nitrogen in the upper atmosphere. (More details here).
We see the amount of carbon-14 that we'd expect for a regular continuous influx of cosmic rays that we do measure. But if all the elements had been made 10,000 years ago, we'd expect about C-14 to be about 1/4 of the total carbon, not the mere 1/1012 of it that we know is produced by cosmic ray collisions.
It turns out that comparing the abundance of isotopes of any element indicates the age of the planet to be between 4,000,000,000 and 5,000,000,000 years.
But what (I can predict this argument) if God created the elements with the isotope distributions intentionally skewed to just look like everything is that old? The old God-is-a-liar and created the young world old to eventually test faith of careful observers argument. I counter this with:
Given God and the Devil, which one has the power to put consistent evidence in every crevice of this and other planets and throughout the universe for every method of observation in every discipline for all interested observers of any faith,
and which one might inspire a few men men to write and edit a book and spread its message eagerly that can be interpreted to contradict that massive universe of evidence?