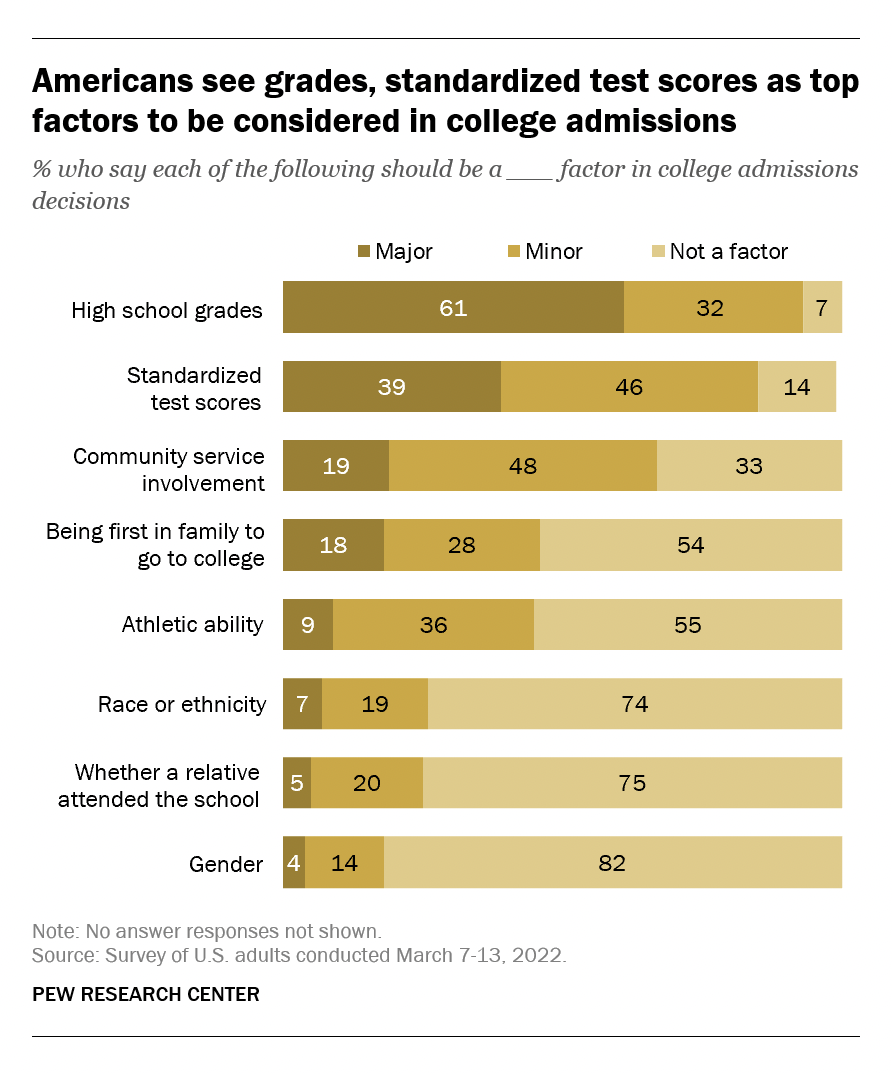
For those of you who are parents, is this how you want sex education taught to your first grader? Is there really a medical school class called "Guessing the Sex of New born Babies"? Sex is anchored strongly to biology. That's what doctors care about. They don't care about "gender" except to the extent that gender means "sex" and only one out of 6,000 babies has an intersex condition. And how is it that when you go to the humane society to adopt a "female" or "girl" dog or cat, they don't look confused? They know exactly what you mean. It's the same thing as doctors, who don't "guess" what sex a baby is, except one out of 6,000 times.
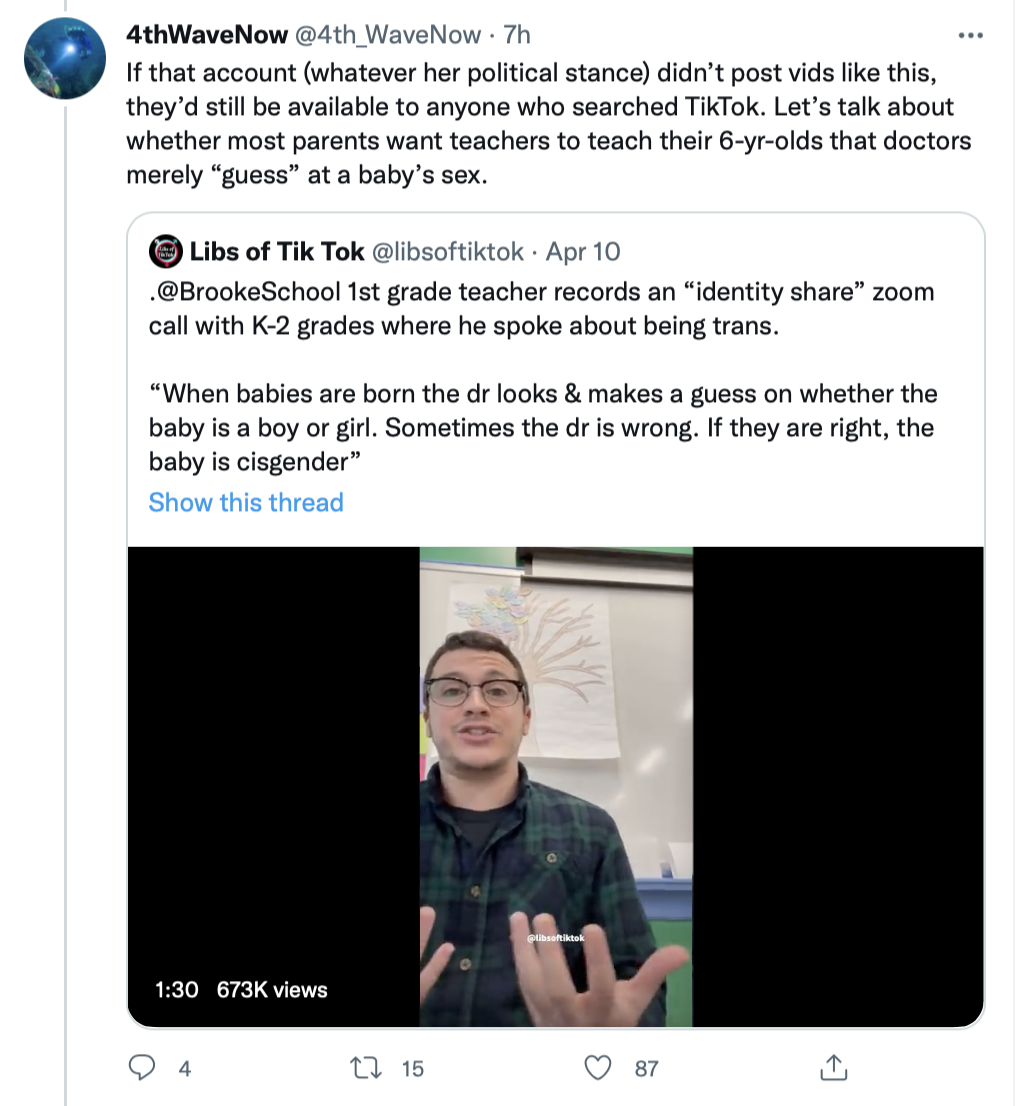
Those who hate "Libs of Tik Tok" are pissed that the creator of that account is holding up the mirror to modern incoherent non-scientific insanity. My kids are now grown, but if I had first graders and I found out that they were being taught this gibberish, I would be outraged. I write these words as a person who has voted almost entirely for Democrats for the past four decades and who has canvassed for Bernie Sanders. If moderate Democrats don't muster up the courage to speak up, they will have earned the red wave that is currently being predicted.