Check out these identical twins:
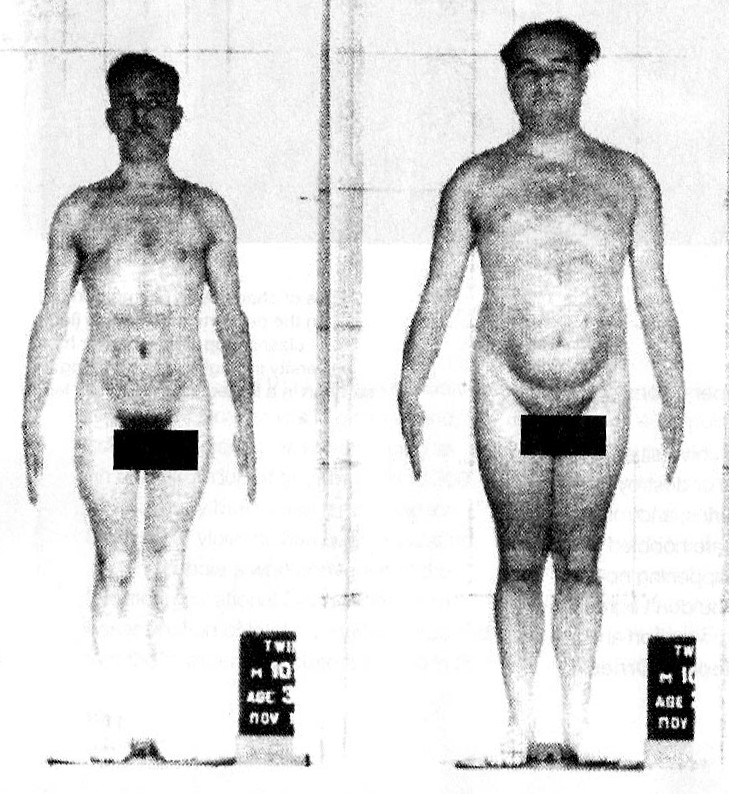
They are really identical twins. This photo is from the November 2006 issue of Discover Magazine. See the related article: “DNA Is Not Destiny The new science of epigenetics rewrites the rules of disease, heredity, and identity.”
Though these two men are genetically identical, they were separated at birth. The man on the left was malnourished for years. Bone structure changes brought about by environmental factors is thus one of many ways (physical and behavioral) in which the environment can dramatically affect the way in which the genes express themselves
As the Discover article points out, the 25,000 genes of our human DNA are widely considered to be an instruction book for our bodies. However, “genes themselves need instructions for what to do, and where and when to do it.” These additional instructions are not in DNA, but
on it, in an array of chemical markers and switches, known collectively as the epigenome, that lie along the length of the double helix. These epigenetic switches and markers in turn help switch on or off the expression of particular genes.
It has long been known that epigenetic switches are critical to the healthy development of organisms. These can be dramatically tweaked by exposure to a vitamin, a toxin or even mothering, altering “the software of our genes in ways that affect an individual’s body and brain for life.” Green tea, for example, has been shown to prevent the growth of cancers.
New research has even …


