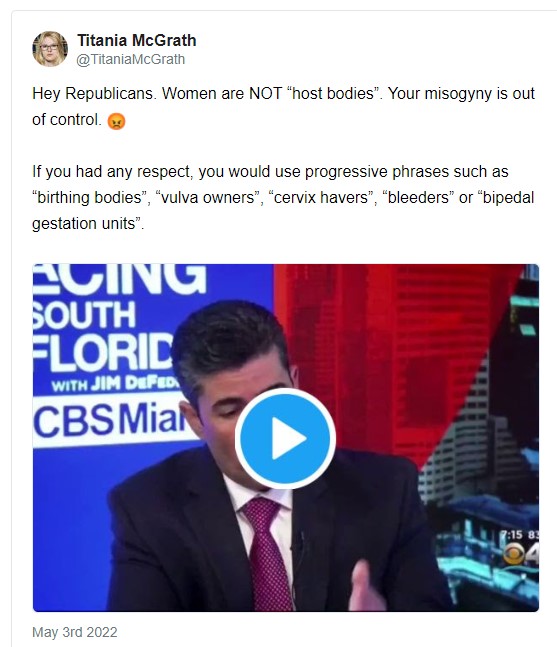
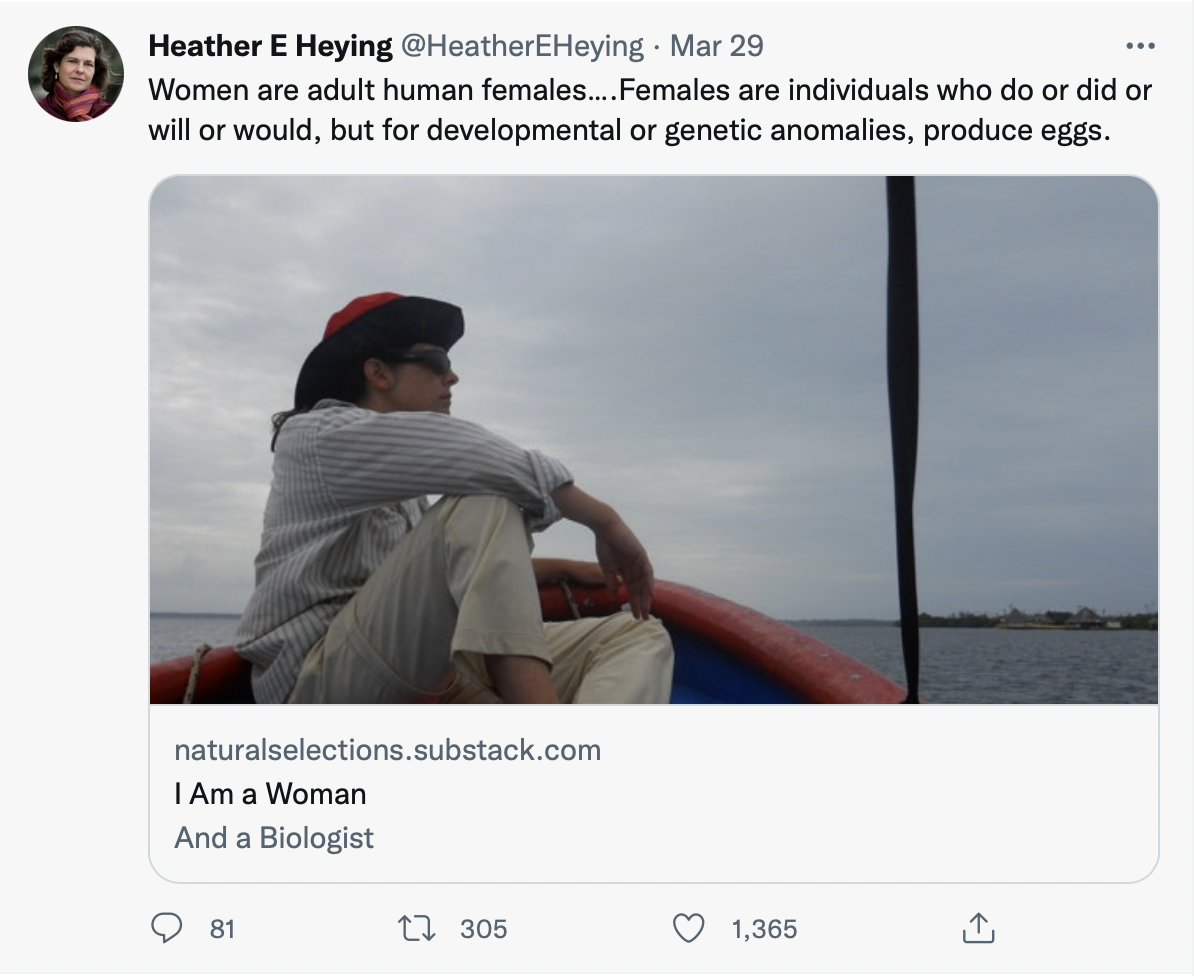
At Common Sense, Zoe Strimpel has written an article titled "How Feminism Got Hijacked. The movement that once declared “I am woman, hear me roar” can no longer define what a woman is. What happened?"
In this article, Strimpel refers to this March 31 2022 Headline in The Washington Post:

What follows is an excerpt from Strimpel's excellent article:
Post-Feminist Feminism has morphed into a dark, strange Anti-Feminism. Anti-Feminism borrows from the language of liberation, but it’s not about liberating women. It’s about pushing women out of college sports. It’s about telling girls they aren’t lesbians or tomboys, but in fact men struggling to find themselves.
It is the madness that led a storied American newspaper to run an anti-woman (or de-woman-ed) headline—garnering roughly 1,400 comments (almost all negative) before shutting down the comments section. It is the trap that ensnared a Supreme Court nominee, who had acquitted herself with great aplomb and suddenly found herself at the end of an ideological cul de sac. To attempt an answer, any answer, to the question—Can you provide a definition for the word ‘woman’?—would be to re-center women, biological sex, the concrete, mundane experience of ordinary, boring, bourgeois and working-class and very poor women the world over. It would be to attempt to undo the hijacking of the feminist cause and to return it to the people for whom that cause was created so many decades ago.
Returning the cause to the people for whom it was created is the only way to save it, and to stop the many discriminations that girls and women still face: domestic violence; the economic and psychological penalty of having babies; the manifold hurts and crimes visited upon countless women in non-Western countries simply for being women. For now, doing anything about all of that is a fantasy. First, we have to honor the actual meaning of words, like woman. We have to insist that those meanings are important. We have to go back, again, to first principles. That is the only way forward.
I will never stop using the word "woman" to refer to the women in my life, whether they be my mom, my daughters, my sisters and my friends. I do so proudly and publicly. I will speak out strongly against those people who use the word "women" only in private (especially liberals who agree with me but who are too cowardly to speak out).
In the meantime, we see headlines like this: "Two inmates at all-women's New Jersey jail are PREGNANT after both had sex with transgender prisoners: ACLU won battle to house 27 trans inmates there."